9 July 2019. By Bill Gates. Never heard of CGIAR? You’re not alone. It’s an organization that defies easy brand recognition. For starters, its name is often mistaken for “cigar,” suggesting a link to the tobacco industry. And it doesn’t help that CGIAR is not a single organization, but a network of 15 independent research centers, most referred to by their own confusing acronyms.
A great example of a CGIAR innovation helping smallholder farmers adapt to climate change is its drought-tolerant maize program. More than 200 million households in sub-Saharan Africa depend on maize for their livelihoods. Maize productivity in Africa is already the lowest in the world. And as weather patterns have become more erratic, farmers are at greater risk of having smaller maize harvests, and sometimes no harvest at all.
In response to this challenge, CGIAR’s International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center or CIMMYT, with funding from our foundation, USAID and the Howard Buffett Foundation, developed more than 150 new maize varieties that could withstand drought conditions. Each variety is adapted to grow in specific regions of Africa. At first, many smallholder farmers were afraid of trying new crop varieties instead of more commonly planted ones. But as CIMMYT worked with local farmers and seed dealers to share the benefits of these new varieties, more and more farmers adopted drought tolerant maize. The results have been life changing for many farming families.
See the full article: You’ve probably never heard of CGIAR, but they are essential to feeding our future
In response to this challenge, CGIAR’s International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center or CIMMYT, with funding from our foundation, USAID and the Howard Buffett Foundation, developed more than 150 new maize varieties that could withstand drought conditions. Each variety is adapted to grow in specific regions of Africa. At first, many smallholder farmers were afraid of trying new crop varieties instead of more commonly planted ones. But as CIMMYT worked with local farmers and seed dealers to share the benefits of these new varieties, more and more farmers adopted drought tolerant maize. The results have been life changing for many farming families.
See the full article: You’ve probably never heard of CGIAR, but they are essential to feeding our future
Related:
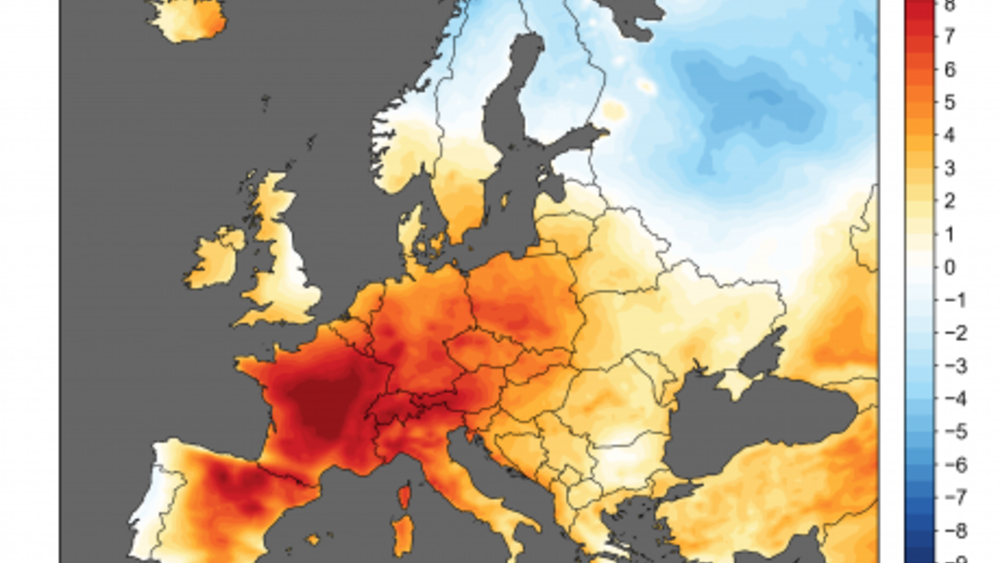
3 July 2019. News release from ICARDA. The heat-wave in Europe poses a significant threat to wheat production across the continent. If a heat-wave like the one recorded these days was to occur 1 month earlier, at the end of May, when the Northern European wheats are in full bloom, it could cause up to 50 percent yield loses, a devastating blow to the European agriculture and food sectors that could cost billions of Euros. 
No comments:
Post a Comment